Without prior knowledge or education on the causes and effects of both bronchitis and emphysema, it can be almost impossible to be able to tell the difference.
The first thing to know about emphysema and bronchitis is that they are two types of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), you should also be aware that often times they coexist.
The symptoms that both diseases consistently emit is chronic breathlessness and other lung related symptoms.
If you begin to notice an influx of breathlessness or any of the symptoms below on a constant basis, then you should talk to your doctor about getting tested for one or both forms of COPD.
Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments for Emphysema and Bronchitis
Defining Emphysema
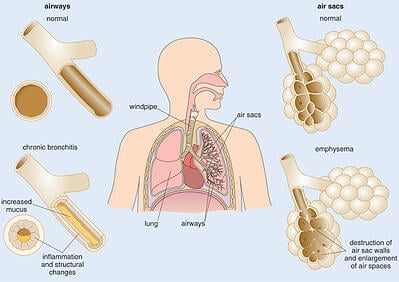
As previously said emphysema is a chronic lung disease, which effects the tiny air sacs (alveoli) at the end of the permanently enlarged airways that become damaged and inefficient. This causes troubles for the lungs because once the air sacs become damaged or destroyed, the once tiny air sacs loose their walls causing them to enlarge. Once this occurs the enlarged air sacs are unable to move a sufficient amount of oxygen into the bloodstream. Which in return causes difficulty breathing or breathlessness, which will progressively get worse. The reason emphysema is so life impacting is because once the air sacs are destroyed, they cannot be healed.
Causes of Emphysema
The number one cause of emphysema is regular cigarette usage, this regular usage causes the inflammatory cells in the lung to be activated. While the other most common cause of this lung disease is excessive exposure to lung pollution. When these occur it causes two problems, swelling within the airways, and secondly enzymes are activated that attack and destroy the lung tissue. There are also cases of emphysema where patients have never smoked a cigarette a day in their life, the cause is a genetic deficiency known as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. This inherited disease attacks all the tiny air sacs (alveoli) throughout the lungs in congruence.
Symptoms of Emphysema
When living with emphysema you should already begin preparing yourself for the disease to get progressively worse over time. Though with regular treatment, doctors visits, and other lifestyle adjustments you can live a happy and active lifestyle with emphysema. The most common symptoms are:
- Breathlessness
- Rapid Breathing
- Wheezing
- Chronic Coughing with, or, without sputum
- Lowered Exercise Tolerance
- Loss of Appetite
- Loss of Weight
Treatment for Emphysema:
- Quitting Smoking
- Pulmonary Rehab
- Oxygen Therapy
- Inhaler Therapy
- Antibiotics
- Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Treatments
Defining Bronchitis
Unlike emphysema which enlarges the air ways and causes damage to the alveoli, bronchitis causes irritation or inflammation in the section of the lung known as the bronchioles. This causes trouble for the patient because the bronchioles connect the trachea (windpipe) to the lungs. The constant irritation causes excess amounts of mucus to be produced, which then clogs the bronchioles making breathing increasingly difficult. When discussing bronchitis with your doctor make sure you know the difference of acute and chronic bronchitis. To put it simplistically acute bronchitis is caused by a cold or other respiratory infections, and will usually clear up within a few days without any long term affects. If you experience frequent bouts with bronchitis then you may have chronic bronchitis, which is a more serious diagnosis that requires medical assistance and is part of COPD.
Causes of Bronchitis
- Acute bronchitis is caused by a virus, usually the same virus that causes the common cold or flu.
- Chronic bronchitis in majority of patients is caused from the use of tobacco cigarettes, exposure to harmful environmental pollutants in the work place, or exposure to toxic gases can also be attribute to an increase of the condition.
Whether you have acute or chronic bronchitis you can experience any one of these symptoms:





