.png?width=560&name=1stclassmed.com%20(3).png)
We have all gotten hiccups here and there, they are a nuisance and can be distracting to us and others, but what are hiccups?
Hiccups are the spasm of our diaphragm and respiratory organs, it is normally caused by irritation of the nerves from our neck to our chest, and that is believed to cause the hiccup.
Causes of these nerve irritations is commonly due to:
- eating too fast
- swallowing air
- chewing gum
- smoking
- eating or drinking too much
- strokes
- brain tumors
- damage to nerves
- some medications
- certain fumes
- anxiety and stress
Though hiccups are a nuisance, it is normally not a reason to go see your doctor, as they often subside on their own within a few minutes of starting.
As they continue to occur for more than 48 hours, it may be time to see your doctor and they may end up prescribing medication or seeing if there is an underlying condition.
It is important to see a doctor when the hiccups are persistent and last more than a few hours, or if they disrupt your eating, sleeping or cause any reflux.
If you have any abdominal pain, fevers, shortness of breath, coughing up blood, or the feeling of your throat is closing up associated with hiccups, see your doctor immediately.
Hiccups can be a sign of a serious medical condition, this is often more common among men than women.
What Is A Hiccup?
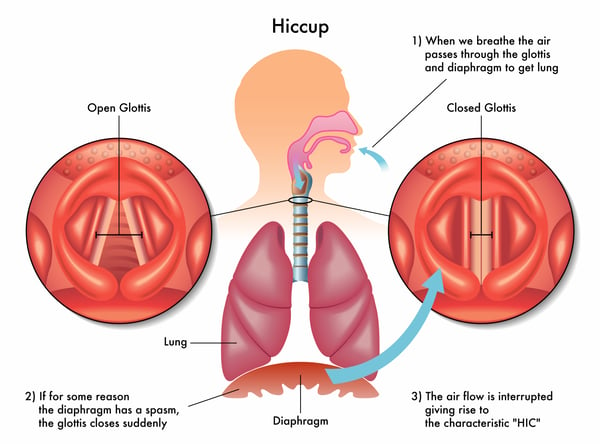
A hiccup is the spasm of your diaphragm, which can cause air to be pulled into your throat, and the closing of your vocal cords, making the “hic” sound.
Your diaphragm is a muscle that separates your chest cavity (containing your heart and lungs) from your abdomen (your stomach and intestines).
It helps with breathing, contracting and relaxing to help oxygen enter and exit your lungs.
If your diaphragm spasms the same time as your larynx (voice box), it results in the closure of the glottis (the middle of the larynx) which causes a rush of air into the lungs, and the hiccup noise we commonly hear.
The medical term for hiccups is synchronous diaphragmatic flutter or singultus (SDF) and it is possible for hiccups to occur individually or consistently.
Commonly hiccups occur for no more than a few minutes every once in a while, but it is possible to have hiccups that last a long period of time, requiring doctor attention.
Any hiccups lasting longer than 48 hours are considered persistent, and it is recommended to seek a doctor after that time.
Hiccups often result from a large meal, alcoholic/carbonated drinks, or sometimes even sudden excitement.
If they continue after a period of time, it is possible hiccups can disrupt your eating, drinking and breathing.
This can cause irritability, fatigue and even weight loss if no change has occurred with the hiccups.
If the hiccups does not resolve itself, it could be because of nerve damage or irritation to your vagus and phrenic nerves.
These nerves run from your neck to your chest and help severe the diaphragm muscle.
The nerves can get irritated or damaged by a hair or something touching your eardrum, a tumor, cyst or goiter in the neck, gastroesophageal reflux, a sore throat or laryngitis.
All of these can upset the nerves which can cause your diaphragm to become irritated or even damaged.
The central nervous system can also play a factor in a chronic hiccups, if the nerves are damaged, infected or if there is a tumor pressing on the nerve it is possible to cause continuous hiccupping.
Central nervous system disorders include encephalitis, meningitis, multiple sclerosis, stroke, brain injury or tumors.
A metabolism disorder as well as drugs can trigger a hiccup, such as alcoholism, anesthesia, barbiturates, diabetes, electrolyte imbalance, kidney disease, steroids, and tranquilizers.
Diagnosis
When you notice you have been hiccupping for 48 hours or more, it is recommended to go to the doctors and get a diagnosis.
If you feel that your hiccups are affecting your sleeping patterns interfere with eating, shortness of breath, vomiting or spitting up blood.
Your doctor will test a few things, such as your balance, coordination, muscle strength, tone, reflexes, and your senses (such as sight, and touch).
If they feel that they cannot diagnose what is causing your hiccups, they may refer you to a specialist, such as an otolaryngologist, gastroenterologist, neurologist, pulmonologist or a psychologist.
Laboratory tests may be done in order to see if there is an underlying medical condition that is causing your hiccups.
Home Remedies
If you are trying to rid yourself of hiccups and have not had them long enough to see a doctor, there are some home remedies to try.
As always, do everything safely and consult your doctor about if any of these are unsafe your you.
- Holding your breath: though it can be difficult, holding your breath (and make sure your lungs are full of air) can help stop hiccups by keeping your diaphragm contracted and it cannot spasm, this can take multiple times in order to stop the hiccups.
- Drinking a glass of cold water quickly: this can be helpful to stop hiccups by calming down your diaphragm and relaxing it.
- Have someone scare you: this classic technique works if you don’t see it coming. By letting someone scare you, it takes a sudden breath in, and contracts your diaphragm.
Though no home remedy has been proven by science, it is worth a shot, as none of the above is too dangerous.
But remember to never try any of these methods on infants, as it can cause harm to the child.
Conclusion
Hiccups are funny, but after the first few hiccups you can easily get annoyed.
Understanding why hiccups happen and possible causes as well as risks can help you better decide if you need to see a doctor or not.
It is possible to also try a home remedy before making an appointment with a doctor, as though they sound silly, they may just work!



